Courses For Mechanical Students | Artem
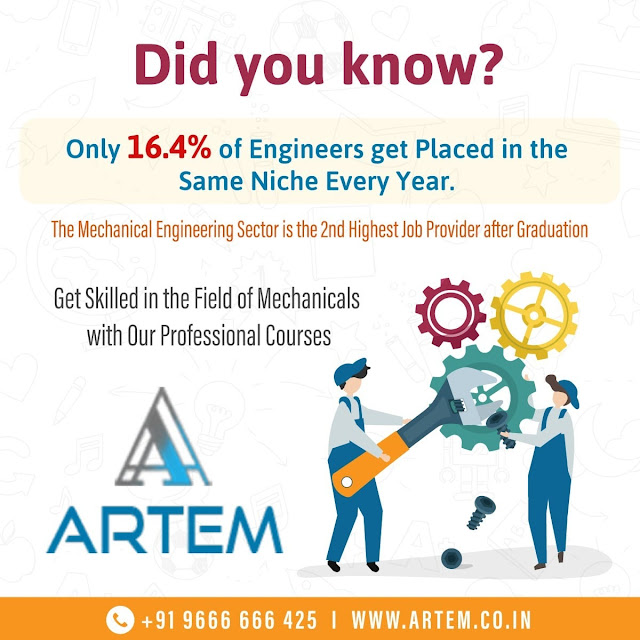
Engineering in its simplest words means – building and designing things that have the capability of solving real-world problems. But due to a lack of proper guidance & opportunity, many engineering students especially in the mechanical field fail to get their dream job. At Artem , we provide mechanical engineering courses that would help the aspirants to get their dream jobs for sure. We cover courses like - 1. ANSYS 2. AUTOCAD 3. ETABS 4. HYPERMESH ANSYS This course is recommended for anyone who wishes to perform Finite Element Analysis (FEA) of different parts/assemblies and basic knowledge on ANSYS Mechanical APDL advanced (MAPDL) software experience. The course focuses on advanced topics such as complex geometries, non-linearities, scripting, convergence debugging, contact options, Sub-modelling, Buckling, Thermal, Modal, results in interpretations, Quizzes, Assignments, & so on. AUTOCAD The AutoCAD course will provide a foundation knowledge to the candidates about the